
Single bonds occur when two electrons are shared and are composed of one sigma bond between the two atoms.
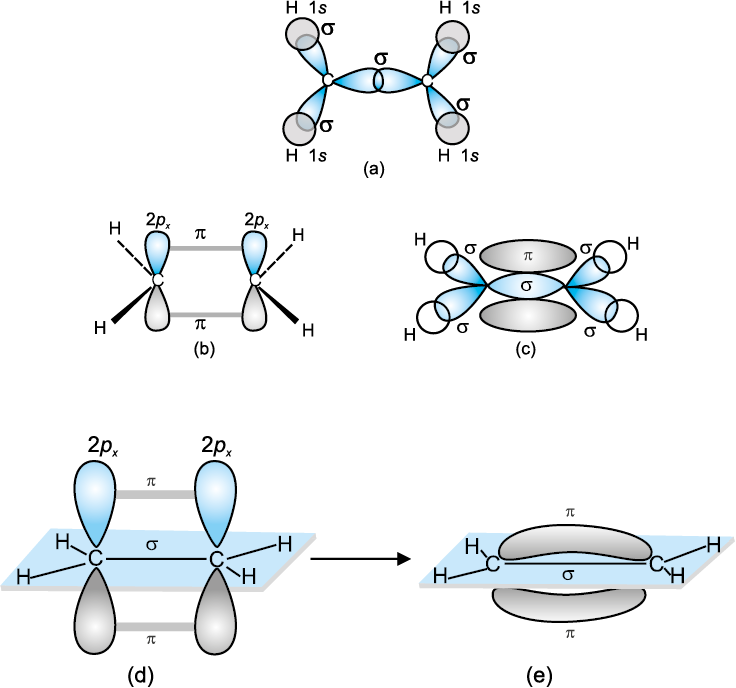
How many valence electrons are in a sigma bond orbital?
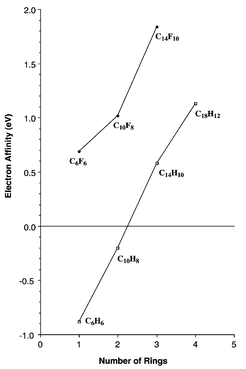
How many π bonds are there in an anthracene molecule?.How many sigma bonds does anthracene have?.How many valence electrons are in a sigma bond orbital?.On further standing of the decanted solution. Low-gradient crystallization by diffusion of n-hexane from an added layer into the blue THF solution of anthracene that is reduced at a potassium metal mirror yields-after three days standing at room temperature-black needles with a violet lustre (see Methods). (THF, tetrahydrofuran TMEDA, tetramethylethylenediamine.) 1c) (see Methods), and stimulated attempts to crystallize even larger aggregates. 1b), to the ion quadruple of two anthracene radical anions connected by a +2 bridge ( Fig. 1a), via the double 6 -half-sandwichs of two ligands on both faces of the anthracene dianion (Fig. 1) ranges from the solvent-separated sodium salt of the bare anthracene radical anion (Fig. The manifold of possible anthracene anion salt structures ( Fig. For instance, if the -hydrocarbon anthracene is reduced in ether or alkylamine solutions at alkali-metal surfaces x, slight modifications of the conditions lead to various reduction products which can be structurally characterized in single crystals (Fig.

They are formed in a multidimensional network of solution equilibria involving electron transfer and contact ion pair formation as well as aggregation, and are often dominated by cation solvation such solvation is known to control numerous chemical reactions, including geochemical and biochemical reactions. Molecular anions M n - and their countercations Met + solv (where Met is the alkali metal) crystallize from aprotic solvents either as solvent-separated n or as solvent-shared solv ion pairs. We expect that the successful crystallization of the ionic solid we report here, and that of a covalent organic compound with a triplet ground state at room temperature, will stimulate further attempts to develop new triplet-ground-state materials for practical use.

Although the spins in this biradical ionic solid are separated by a considerable distance, density functional theory calculations indicate that the triplet ground state is 84 kJ mol -1 more stable than the first excited singlet state. Its electronic ground state is shown experimentally, using temperature-dependent electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy, to be a triplet. Here we report the anaerobic crystallization of an ionic organic aggregate-a contact ion septuple consisting of a fourfold negatively charged 'tripledecker' of three anthracene molecules bridged by four solvated potassium cations. The formation of supramolecular aggregates can even be exploited to generate aromatic hydrocarbons that carry four negative charges and crystallize in the form of organic poly(metal cation) clusters or helical polymers. Aggregates containing metal cation clusters 'wrapped' by lipophilic molecular anions have, for example, been shown to be kinetically stable and soluble in nonpolar liquids such as saturated hydrocarbons. Havlas Ĭrystalline supramolecular aggregates consisting of charged organic molecules, held together through metal-cluster-mediated Coulomb interactions, have attracted interest owing to their unusual structural, chemical and electronic properties.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
